Have a W-BAD Day
World Benzodiazepine Awareness Day (W-BAD) is July 11th. It seeks to raise awareness about iatrogenic (medically) caused benzodiazepine dependence and adverse effects associated with the benzo withdrawal syndrome. This can occur with up to 90% of individuals who have used them daily for over 3 or four weeks. Globally, benzodiazepines are among the most widely prescribed drugs. According to PsychCentral, the benzodiazepines Xanax (alprazolam) and Ativan (lorazapam) were in the top ten most prescribed psychiatric drugs in the U.S. for 2018. An article in the American Journal of Public Health, said between 1996 and 2013 the number of U.S. adults filling a benzodiazepine prescription increased by 67%. And they were involved in 31% of the fatal overdoses in 2013.
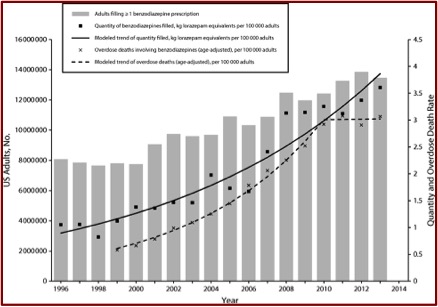
The Bachhuber et al. study in the American Journal of Public Health reported that the number of U.S. adults filling a prescription for benzodiazepines increased from 8.1 million to 13.5 million between 1996 and 2013. The total quantity of benzodiazepines dispensed more than tripled during the same time period. And the rate of overdose deaths involving benzodiazepines increased from .58 per 100,000 adults to 3.07 per 100,000 before plateauing in 2010. See the following chart from the study. The researchers gleaned the data reported here from the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey.
 The New England Medical Journal cited the same study in a February 2018 article, “Our Other Prescription Drug Problem.” The authors added that U.S. prescribers wrote 37.6 benzodiazepine prescriptions for every 100 individuals. Three quarters of the deaths involving benzodiazepines also involved an opioid. Yet, “Despite the increased risk of overdose in patients taking both benzodiazepines and opioids, rates of coprescribing nearly doubled, increasing from 9% in 2001 to 17% in 2013.”
The New England Medical Journal cited the same study in a February 2018 article, “Our Other Prescription Drug Problem.” The authors added that U.S. prescribers wrote 37.6 benzodiazepine prescriptions for every 100 individuals. Three quarters of the deaths involving benzodiazepines also involved an opioid. Yet, “Despite the increased risk of overdose in patients taking both benzodiazepines and opioids, rates of coprescribing nearly doubled, increasing from 9% in 2001 to 17% in 2013.”
Another growing problem is the distribution of benzodiazepine analogues in the illicit drug market. “Manufactured in clandestine laboratories in the United States and elsewhere, these drugs are indistinguishable from prescription benzodiazepines and are potentially as deadly as the synthetic opioid analogue fentanyl.” I’ve heard of an individual who blacked out and landed in the hospital after ingesting a benzo analogue. “Clonazolam, an analogue of clonazepam that is akin to a combination of alprazolam and clonazepam, is so potent that it needs to be dosed at the microgram level using a high-precision scale to prevent accidental overdose.”
Benzodiazepines have proven utility when they are used intermittently and for less than 1 month at a time. But when they are used daily and for extended periods, the benefits of benzodiazepines diminish and the risks associated with their use increase. Many prescribers don’t realize that benzodiazepines can be addictive and when taken daily can worsen anxiety, contribute to persistent insomnia, and cause death. Other risks associated with benzodiazepines include cognitive decline, accidental injuries and falls, and increased rates of hospital admission and emergency department visits.
Concern with the over use and over prescribing of benzodiazepines is truly a global issue. Look at the Statistics page for W-BAD to see dozens of surveys and studies from around the world. Some highlights include: Japan has the highest consumption rate of benzodiazepines in the world. In Thailand, 45% of GPs admitted their prescription of benzodiazepines in the previous year had been excessive. Positively, in Denmark it is illegal to prescribe a benzodiazepine for longer than four weeks. Afterwards, a full medical re-evaluation is needed to assess their continued use. Not surprisingly, benzo use in the Danish population decreased significantly from 1997-2008.
On the front page for W-BAD, you can see a short video about “The risks of taking benzodiazepines.” You’ll learn that experts estimate that 60% of people taking benzodiazepines for more than 2 to 4 weeks will experience withdrawal or adverse effects. About 30% will experience severe withdrawal or adverse effects. And this can even happen on low doses. There are also links to other YouTube videos, like “The 5 Myths of Benzo Withdrawal.”
Anna Lembke, a doctor and associate professor of psychiatry at Stanford, described receiving a call about one of her patients who almost died from overdosing on a benzodiazepine. He had taken clonazolam, a designer benzo compound first synthesized in 1971. It is a combination of clonzapam (Klonopin) and alprazolam (Xanax) and it is said to be 2.5 times more potent than Xanax. Her patient knew it was potent, but still overdosed. He said the amount he took “wasn’t enough to cover a fourth of my pinkie fingernail. I thought I was safe.” She was the lead author of the above linked NEMJ article.
Highly potent drugs like these designer benzodiazepines are a growing trend among those seeking a new high, fueled in part by doctors overprescribing benzodiazepines without appreciating their addictive potential. Just as overprescribing opioids contributed to the use of heroin and illicit fentanyl and related deaths, overprescribing benzodiazepines may herald the dawn of a new era of illicit and deadly benzodiazepines. Benzodiazepines work well to ease anxiety or insomnia when used intermittently and for less than a month at a time. When taken daily for an extended period of time, they stop working and can make anxiety and insomnia worse. Most doctors don’t realize how addictive benzodiazepines can be for some people and, because they don’t know better, prescribe them long term and without safety monitoring, like checking the prescription drug monitoring database. In addition to addiction and death, long-term use of benzodiazepines can also contribute to cognitive decline, accidental injuries, and falls.
She cautioned individuals taking benzodiazepines daily to talk to their doctor about starting a slow taper. “It’s important to go slowly, because abruptly stopping a benzodiazepine can precipitate life-threatening withdrawal.” She added that if you are a parent and notice a precision laboratory scale in your child’s bedroom, or see mysterious packages arriving for them, “get worried fast.”
Writing for Mad in America, Marjorie Meret-Carmen wrote of “My Ativan Affair and the Aftermath.” She was first prescribed Ativan eleven years ago to help her sleep and cope with her dementia-declining husband. She received no warnings about potential adverse effects from regular use. He died in 2009, but she continued using Ativan until January of 2012, where she tried a short-term residential treatment center to withdraw from the medication. Two week afterwards, she began experiencing Protracted Acute Withdrawal Syndrome (PAWS).
Until the beginning of 2015, I lived 24 hours a day, 7 days a week flu-sick, of a magnitude harking back to the worst morning sicknesses with each of my pregnancies. That was the year I was well enough to act on what was becoming a ‘mission’ — to find the common denominators in benzodiazepine toxicity and protocols to help people withdraw and get on with their lives.
That mission eventually included the organization of the International Benzodiazepine Symposium in September of 2017. “Something I decided to sponsor once I realized the medical practitioners I trusted did not know a damn thing about a long-term relationship with a benzodiazepine.” There is a link to a fifteen-minute video synopsis of the conference, which she hopes to expand into a full-length documentary. Within the video, you learn that since 1989 there has been a 4,900% increase in spending on psychiatric drugs in the U.S., from $800 million to $40 billion. Common withdrawal symptoms from benzodiazepines include: moderate to severe depression; extreme anxiety; poor memory; sensory hypersensitivity; heart palpitations; sweating, night sweats; and muscle twitching.
My sincere message to those whose vitality and lives have been sapped and zapped by this iatrogenic dis-order: most of us DO recover! And even if it is not without some benzo remnants lodged in our cellular memory, what we learn about our own resilience will guide us to places in our lives we didn’t expect to reach.
The Ashton Method or Ashton Manual was mentioned in the video. Dr. Heather Ashton wrote “Benzodiazepeines: How They Work and How to Withdraw,” which has become known as “The Ashton Manual.” A digital copy is available here on benzo.org.uk for free. A printed copy can be ordered. You can also watch “Dr. Heather Ashton- Benzodiazepine Withdrawal” and other videos about the Ashton Method on YouTube. It has become the standard reference for benzodiazepine tapering.
A group of Canadian healthcare professionals led by Dr. Kevin Pottie proposed new clinical guidelines to safely deprescribe benzodiazepines in “Deprescribing benzodiazepine receptor agonists.” You can also read a summary of the above article in “New Clinical Guidelines on Deprescribing Benzodiazepines.” The authors qualified their tapering recommendations primarily for patients who use benzos to treat primary insomnia (insomnia on its own). The guideline “does not apply to those with other sleep disorders or untreated anxiety, depression, or other physical or mental health conditions that might be causing or aggravating insomnia.” They recommend that deprescribing (slow tapering) be offered to all elderly adults taking benzos, regardless of duration of use and to other adults who have used them for more than four weeks.
Choosing Wisely Canada does not recommend BZRAs [benzodiazepines] as a first-line treatment for elderly patients with insomnia, as common side effects include increased risk of falls and accidents, memory problems, and daytime sedation. Furthermore, long-term BZRA use is associated with heightened risk of developing a physical or psychological dependence. Canadian family physicians, pharmacists, nurses, and geriatricians classified BZRAs as the “most important medication class for developing a deprescribing guideline” due to the adverse effects found in long-term use.
The Canadians developed an algorithm and a client information pamphlet to assist clinicians in the deprescribing process. You can find links for both in “New Clinical Guidelines on Deprescribing Benzodiazepines.”
You can read other articles about problems with benzodiazepines and World Benzodiazepine Awareness Day (W-BAD) here on this website: “It Takes Away Your Soul” and “Are Benzos Worth It?”

