I confess, I am not much of a listener of Contemporary Christian Music (CCM). So I had never heard of the CCM artist Kari Jobe or her music until someone asked me about a theological controversy that is making the rounds online about one of her songs, titled Forever. Apparently, the dispute is over a reference in her song to Jesus as the Son of God descending into hell where He defeated the enemy. The person was asking me to see whether I thought that lyric was heretical, and whether Jobe was spreading heresy. My initial reaction was to recall that some versions of the Apostles’ Creed made a similar claim and say that those who are critical of Jobe and her song seemed to be majoring on minor points.
Here is a description of one view of the controversy written by Jeff Maples on his blog, Pulpit & Pen: “Popular Charismatic Worship Artist, Kari Jobe, Teaching Dangerous Heresy.” Maples began by criticizing the Outcry 2016 music festival that will be held in several U.S. cities this year. Kari Jobe is part of the tour. He said: “Now, I’m not exactly sure who these people are worshiping, but it isn’t Jesus. Yet, thousands of Christians are blindly sending their children to partake in this evil.” This is provocative stuff to be saying about the participants of the Outcry 2016 and those who attend it.
His beef seemed to be focused primarily on something called the New Apostolic Reformation (NAR), which he said is a movement that elevates experience above doctrinal truth. Whether NAR is or is not heretical is not the focus here. Someone who wants more information on the movement or its beliefs can easily find discussions online. To get you started, try a Fresh Air podcast in 2011, “The Evangelicals Engaged in Spiritual Warfare”; or a Charisma News response to the NPR interview and article: “The New Apostolic Reformation Is not a Cult” by C. Peter Wagner. Also try “New Apostolic Reformation” on Wikipedia.
In his article, Maples quoted the lyric from Jobe’s song that he saw as offensive:
One final breath He gave
As heaven looked away
The Son of God was laid in darkness
A battle in the grave
The war on death was waged
The power of hell forever broken
Also there is a YouTube clip embedded on the page where Jobe said her favorite part of the song was the part that talks about the time in between the cross and the resurrection when “Jesus was in hell … defeating the enemy … taking those keys to death and hell and the grave to be victorious over that when he rose from the dead.” Maples then equated this with an old heresy he said is found in the Word of Faith circles, that Jesus died spiritually and was “born again” after defeating Satan in hell. Personally, I’m not a fan of the teachings of Joyce Meyer or Kenneth Copeland, who Meyers quotes as promoting this heresy. But it seems to me the “culprit” behind Jobe’s lyric is the Apostle’s Creed rather than the Word of Faith movement.
The Apostles’ Creed has been a confessional element of orthodox Christian belief since the times of the early church. Ambrose and Augustine suggested repeating it in daily devotions. Luther saw it as one of three binding summaries of belief. Calvin divided his Institutes into four parts that corresponded to the Apostles’ Creed. See “Christian, What Do You Believe?” for more background on the Apostles’ Creed.
J. N. D. Kelly, in Early Christian Creeds, pointed out that the first appearance of saying that Jesus “descended to hell” appeared in the Aquleian version of the creed referred to by Rufinus, a fourth century monk and theologian, in his Commentary of the Apostles’ Creed. There he noted the phrase “He descended into hell” was not part of the Roman Creed (See “The Old Roman Creed”) or those of the Eastern (Oriental) churches. Nevertheless, it seemed to be implied in saying that Jesus was buried. Kelly said the clause was also present in some Spanish creeds of the sixth century and Gallican creeds of the seventh and eighth centuries.
Rufinus remarked in his commentary that Jesus descending into hell was foretold in the Psalm 22, classically seen as intimately associated with the passion of Christ. The first words of the Psalm, “My God, my God, why have you forsaken me?” are cried out by Jesus as he was dying (Matthew 27:46; Mark 15:34). Psalm 22:7-8 is alluded to in Matthew 27:39, 43, “All who see me mock me; they make mouths at me; they wag their heads; He trusts in the Lord; let him deliver him!” The final words of the Psalm, “he has done it” were said in Hard Sayings of the Bible to have been alluded to by Jesus in John 19:30 as he bowed his head and died: “It is finished.” Rufinus saw similar references to a descent into hell in Psalm 22:15, “you lay me in the dust of death”; Psalm 30:3, “O Lord, you have brought up my soul from Sheol; you restored me to life from among those who go down to the pit”; and Psalm 30:9, “What profit is there in my death, if I go down to the pit?”
Tom Macy also expressed concern with Jobe’s reference to Jesus descending into hell in his article, “Did Jesus Go to Hell?” Macy said it was bad theology that taught an error striking at the heart of understanding the death and resurrection of Jesus. He said it taught the battle was not won on the cross. Rather, the real battle took place in hell between the death and resurrection of Jesus. “That is what seriously distorts the truth and why this song must not be used.”
A further example of the confusion arising from this reference to a descent into hell in the Apostles’ Creed is in this short video by Garrett Kell from Capitol Hill Baptist Church. I don’t concur with his explanation, but it does show how wild speculation creeps in to explain difficult passages of the Bible. Macy attributed the root of this confusion to Roman Catholic teaching. He then referenced Wayne Grudem’s Systematic Theology to explain passages that have been used to support Jesus’ decent into hell.
Fanciful interpretations of difficult passages must not override the declarations from the cross definitively showing that Jesus did NOT spend Saturday in hell, was NOT fighting Satan to finish the work of salvation, was NOT preaching a second chance salvation or simply condemning to those in hell. Jesus was with the repentant thief in Paradise in the presence of the Father.
And yet, the descent into the underworld was specifically mentioned by: Ignatius, Polycarp, Irenaeus, Tertullian and others, according to Kelly. “The belief that Christ spent the interval between His expiry on the cross and His resurrection in the underworld was a commonplace of Christian teaching from the earliest times.” One strand of patristic teaching thought Jesus himself hinted at it when he said in Matthew 12:40 that the scribes and Pharisees seeking a sign would get only the sign of the prophet Jonah: “For just as Jonah was three days and three nights in the belly of the great fish, so will the Son of Man be three days and three nights in the heart of the earth.”
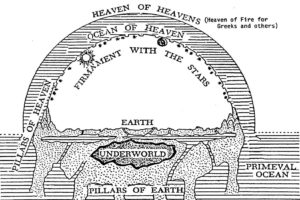
Attempts to explain where Jesus was when his body was in the tomb ask space and time-oriented questions about something that occurred beyond the space and time of the created universe. The answer can’t fit within the cosmos in which we live and move and have our being. And yet, we still wonder where Jesus was when he wasn’t with his body in the tomb. The question says more about us, and our view of the cosmos, than it does about what actually happened to Jesus between about 3 pm Friday afternoon and early Sunday morning. In a similar way, the addition to the Apostles’ Creed of Jesus descending into hell, and the Old and New Testament passages supposedly referencing the same, tell us more about how the people of Biblical times viewed the cosmos than where Jesus was between his death and resurrection.
In his book, Scripture and Cosmology, Kyle Greenwood described how ancient Hebrew cosmology of a three-tiered universe of the heavens, earth and sea had a place for the underworld or the abode of the dead—Sheol. “When people died, they were buried in the ground, and their bodies remained in Sheol, the abode of the dead.” This three-tiered cosmology was shared by other Near Eastern cultures. “It was the abode of the dead, the final resting place beneath the earth for all who once lived.”
On the BioLogos website is a series of blog articles on a scholarly paper by Brian Godawa, “Mesopotamian Cosmic Geography in the Bible.” Here is a link to Part 4 of that series where there is a discussion of Sheol; here is a link to Godawa’s entire paper. The following quotation can be found under either link.
Sheol was the Hebrew word for the underworld. Though the Bible does not contain any narratives of experiences in Sheol, it was nevertheless described as the abode of the dead that was below the earth. Though Sheol was sometimes used interchangeably with “Abaddon” as the place of destruction of the body (Prov. 15:11; 27:20), and “the grave” (qibrah) as a reference to the state of being dead and buried in the earth (Psa. 88:11; Isa. 14:9-11) it was also considered to be physically located beneath the earth in the same way as other ANE worldviews.
The New Testament was written during a time of transition to an Aristotelean cosmology of spheres within rotating spheres. “In time Aristotelean cosmology and biblical faith became inseparable, not because Aristotle was a Christian, but because his system was easily reconciled with biblical anthropology and monotheism.” While the idea of Sheol or the grave underwent some major changes in the Christian era, Aristotelean cosmology didn’t require an abandonment of the idea that beneath the surface of the earth was a region where the dead went. Greenwood added this shows up conspicuously within the Apostles’ Creed.
The added phrase of “descended to hell” to the Apostles’ Creed is then simply making clear that Jesus truly died. Like all people, the humanity of the Son of God died. Not only was he crucified and buried, as it was said within the Roman Creed; Jesus was crucified [dead] and buried [He descended into Hell]. So on the third day, He would arise from the dead; the grave; Sheol. In other words, he would live again. This is the promise of faith in Christ. He reversed the irreversible, according to the ancient thinking about death. I think Kari Jobe can sing about it Forever, if she likes.